BY DANIELA GIRALDO – APRIL 22, 2024
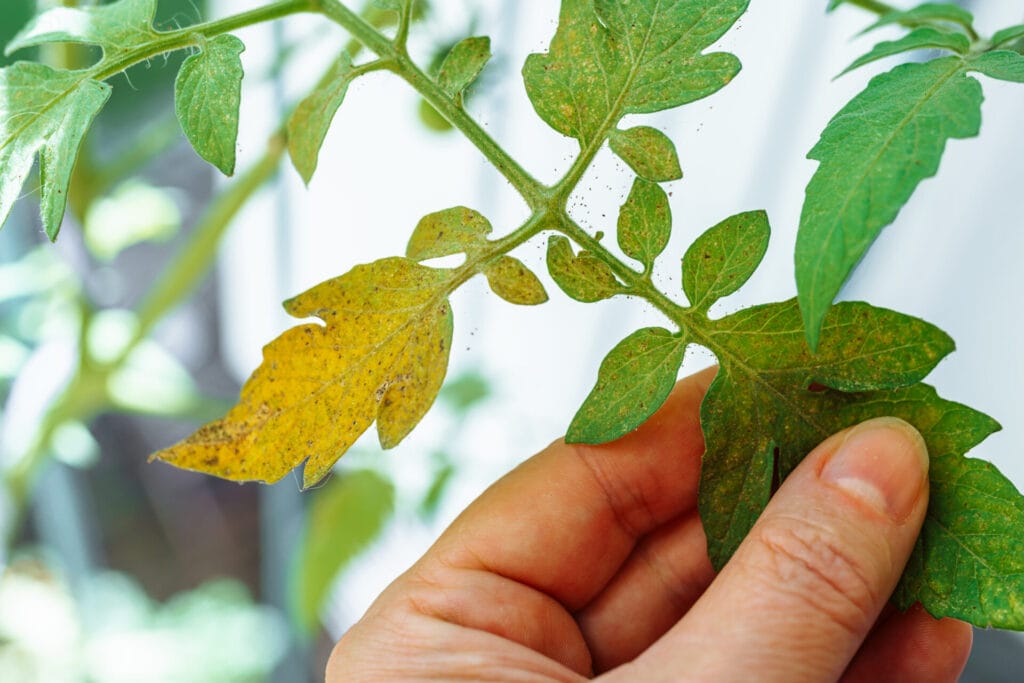

In the world of gardening and agriculture, plant health is paramount. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener, a budding horticulturist, or a commercial farmer, understanding how to optimize plant health is essential for success. From providing vital nutrients to warding off pests and diseases, maintaining robust plant health ensures bountiful harvests and thriving greenery. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of plant health, exploring everything from soil health to pest management, and offering practical tips to help your plants flourish.
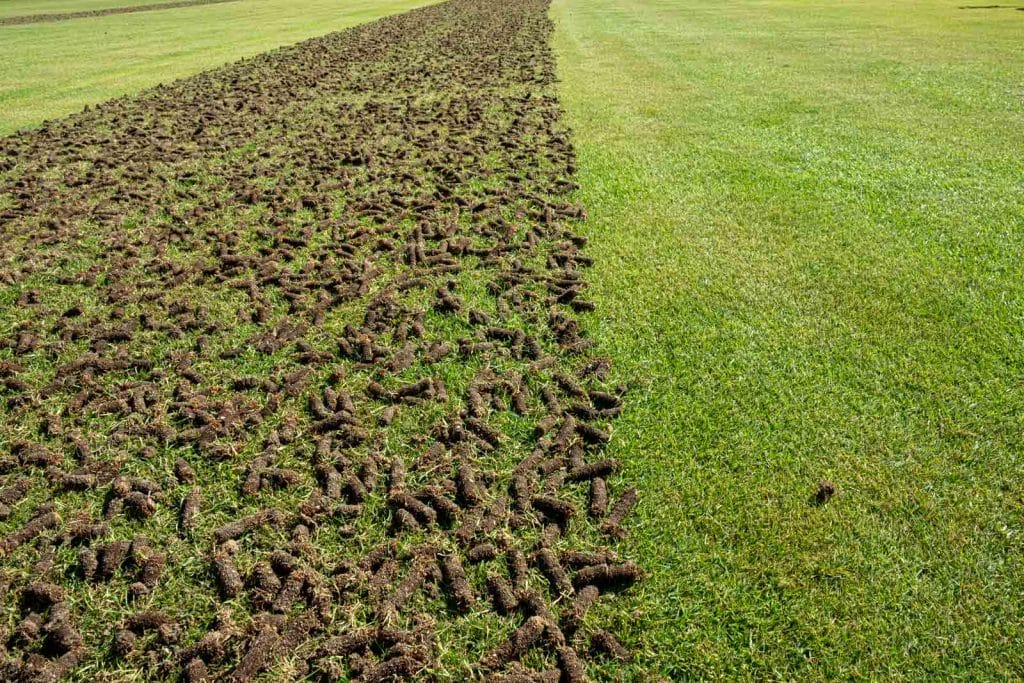
The foundation of plant health lies in the soil. Healthy soil teems with life, providing essential nutrients, water, and support to plants. Soil health is influenced by various factors, including texture, structure, pH level, and organic matter content. To promote soil health, consider the following:
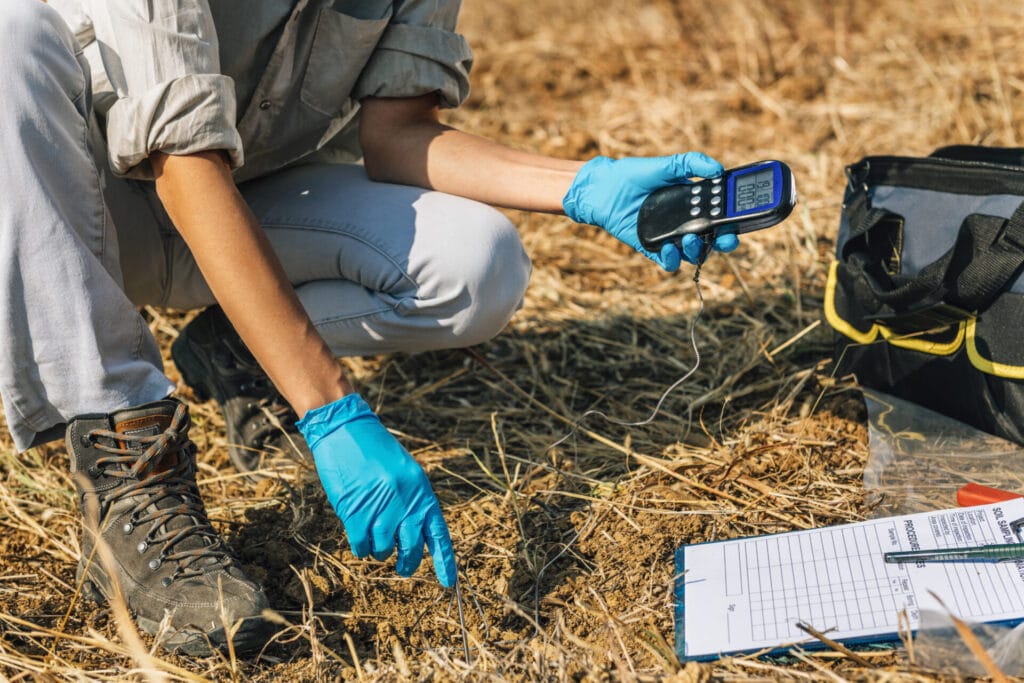
1. Soil Testing: Conduct regular soil tests to assess its pH level and nutrient content. Based on the results, you can adjust fertilizer applications to meet your plant’s specific needs.

2. Organic Matter: Incorporate organic matter such as compost, manure, or mulch into the soil to improve its structure and fertility.

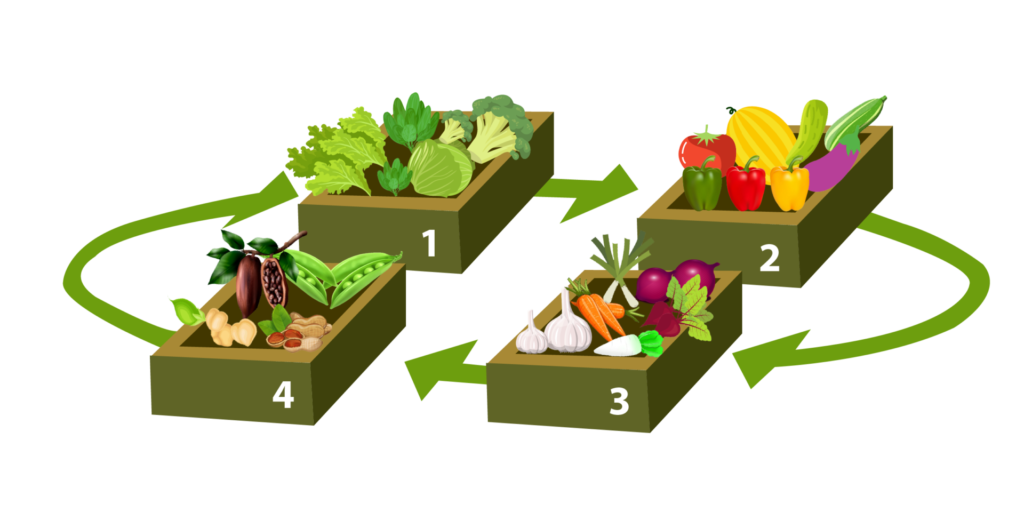
3. Crop Rotation: Practice crop rotation to prevent nutrient depletion and minimize the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
4. Soil Aeration: Ensure proper soil aeration by avoiding compaction and incorporating techniques such as tilling or aerating.

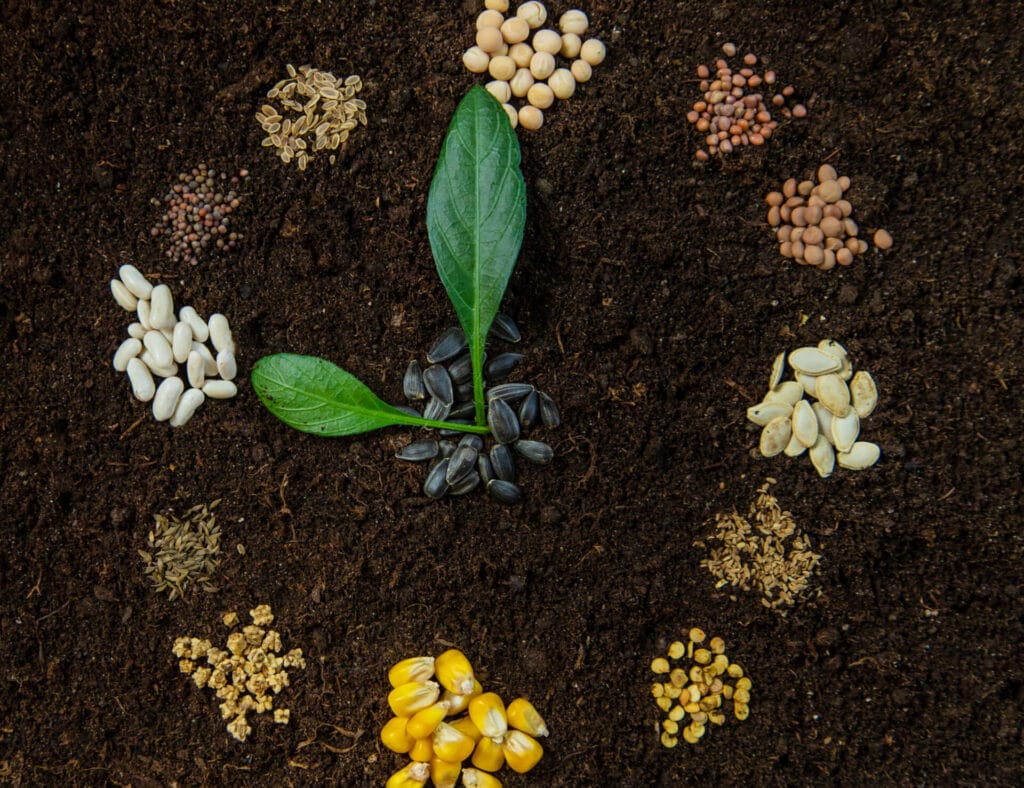
Plants require a balanced diet of essential nutrients to thrive. Macronutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with micronutrients like iron, zinc, and magnesium, play vital roles in plant growth and development. To optimize nutrient management:

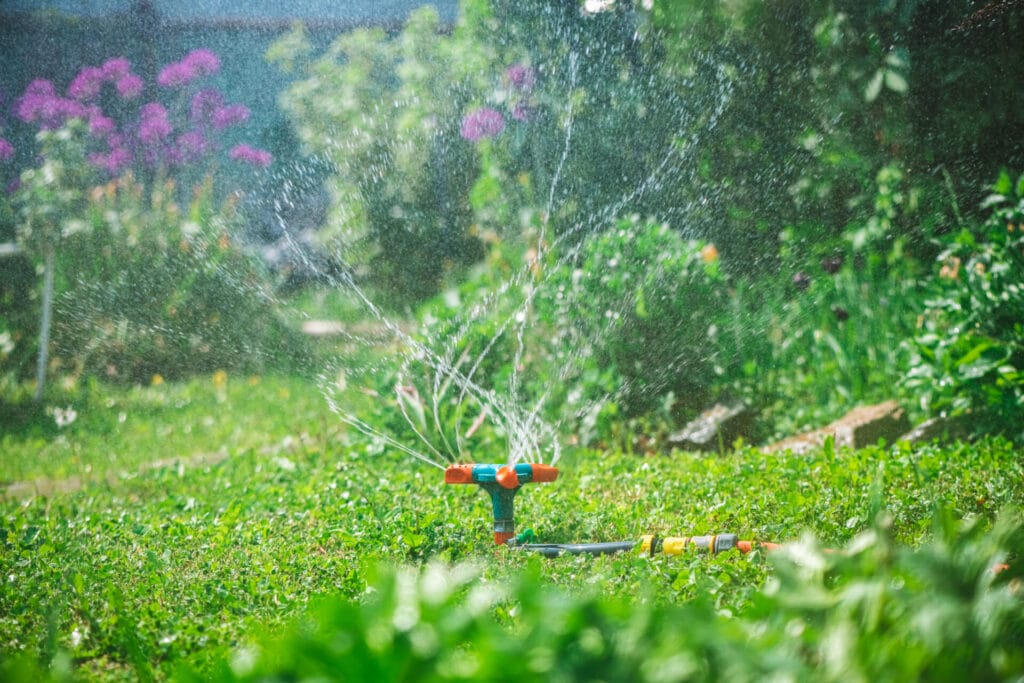
Proper watering is crucial for plant health, as both drought and overwatering can lead to stress and damage. To water your plants effectively:

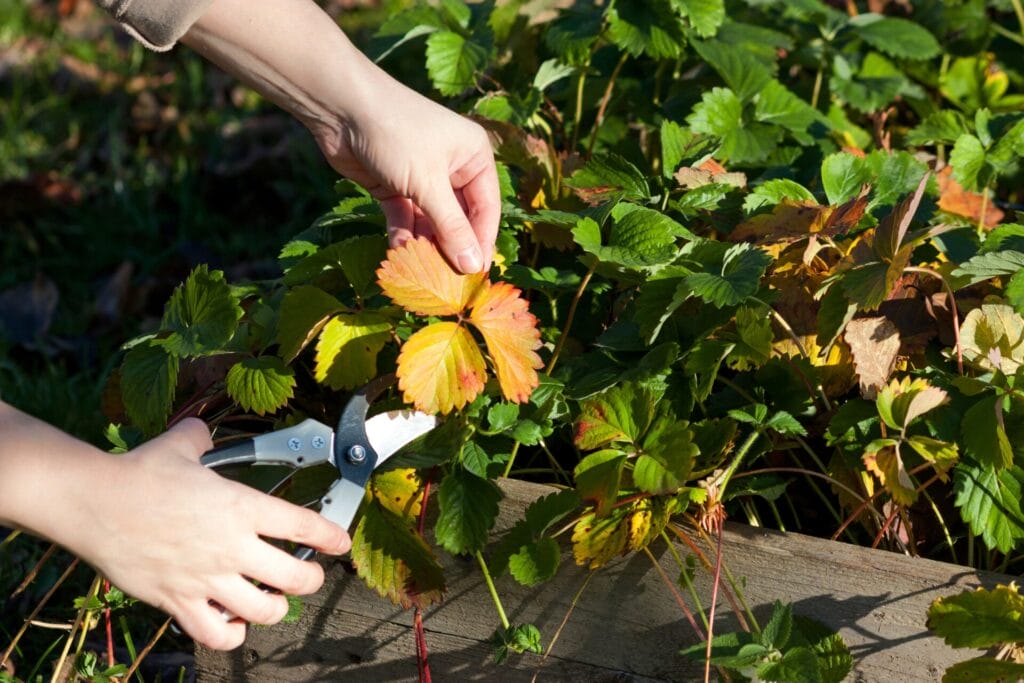
Pests and diseases pose significant threats to plant health, but proactive management strategies can help minimize damage. Here are some tips for effective pest and disease management:

Plant health is a multifaceted endeavor that requires attention to soil quality, nutrient management, water supply, and pest control. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide and staying vigilant in monitoring your plants’ health, you can create an environment conducive to robust growth and flourishing gardens. Remember, healthy plants not only beautify our surroundings but also contribute to a sustainable and vibrant ecosystem.
Share this post:
Check other topics that may help you get more insights for your project:



